25 Mar And the winner is …
Preamble
The intestine is well known to be our second brain and nearly 500 million neurons line our intestine (20 times less than our brain).
But in the history of humanity was not the intestine our first Brain? The first primitive organisms were a simple digestive tract!
Our current brain has developed to help us find food, it’s a division of tasks otherwise we would spend our lives digesting!
Let’s go back to 2 million years ago with the arrival of the domestication of fire and the invention of the « barbecue » which was a revolution for humanity.
Cooking is a pre digestion and facilitates the assimilation of food and therefore as the first brain was less busy our current brain was able to develop and grow without major change for the rest of the body.
The 2 brains will then communicate, this is called neurotransmission.
Serotonin is one of the words exchanged. It signals that resources are available which translates in the brain to meaning ‘wellness’ and regulation of digestion and the immune system in the gut. The serotonin that manages our emotions is also produced in the intestine!!!
Between our 2 brains there is the vagus nerve which is the information highway between these 2 organs, but serotonin passes from one to the other through the blood.
We knew that our emotions could interfere with our gut, but the reverse is true.!!
Irritable bowel syndrome is a communication problem between the two brains. If 10% of the world population suffer from major digestive disorders, no functional assessment poses a problem (colonoscopy, scanner, etc.)
The Technical University of Munich thinks that irritable bowel syndrome comes from the wall of the intestine which is itself very innervated.
Sick patients have a hypersensitive or hyper-permeable wall caused by stress or other traumatic events causing a kind of neurosis of the intestine.
Freud’s unconscious would be in our belly.?
We see that the belly and the head could share their disease!!
Parkinson ‘s disease, for example, would have an intestinal origin. Its first symptoms are often intestinal like diarrhea or digestive like loss of taste.
As it starts at the bottom (gut) and gradually goes up (brain), the researchers showed that the lesions on the neurons of the intestine were the same as those on the neurons of the brain later on.
Many neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s disease, Charcot’s disease) or autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis) could have these same origins where the gut link to the immune system will initiate and create the chronicity of the disease.
In addition, bacteria make man a real ecosystem. We have a little more bacteria in us than cells!
Bacteria provide us with about 30% of our energy needs and they regulate, educate, and inform the immune system of risks (pathogenic bacteria, Viruses, Toxins or toxic chemicals).
A baby’s gut is sterile before birth and the bacteria it ingests early in life will create its gut fingerprint, but food, environment, and antibiotics have an impact on that fingerprint.
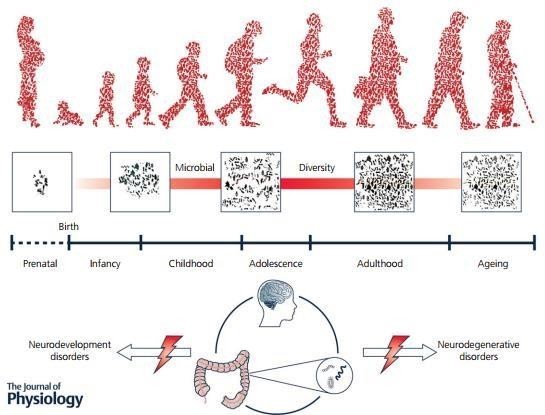
There would be 3 types of enterotype in humans but is there an ideal recipe?
We know certain germs present in normal humans but almost absent in obesity or diabetes, heart
problems, cancers……
Testing a patient’s microbiota could reveal diseases like a blood or urine test does today
We know too that child born caesarean section, who don’t get mother bacteria, has more risk on Obesity, Autism, allergy……
We will now try to understand the role of the intestine in the broad sense in the emerging of chronic diseases
Chronic diseases are multifactorial, always involving a genetic component and immunological and toxic components, linked to the « environment ». This term applies to bacteria, viruses, chemical agents… which are in contact with the microbiota of our mucous membranes. Any excessive passage of bacterial constituents and other toxins will lead to immune activation which, in patients suffering from chronic conditions, always takes up the pathway of stimulation of self- reactive clones attacking the target tissues.
We consider that these diseases are partly due to a close communication between the intestine and the brain via the neurons as well as to a mucosal hyperpermeability linked to the passage of bacterial or other constituents reactivating the immune system and having by themselves toxic effects.
Part of our approach consisted in identifying antibodies circulating in the serum of patients recognizing precise antigenic targets. Antibodies are becoming indirect means of understanding the precise mechanisms linked to these pathologies.
The immune system “monitors” each constituent of the biological self and will thus integrate any modification.
The cause and maintenance of chronic diseases are generally not due to chromosomal abnormalities or gene mutations but to gene overexpression or dysfunction of certain genes.
Genetic predisposition makes us sensitive to « environmental » antigens such as bacteria, viruses, toxins, vaccines, etc. which, after a time (+ or – long) will lead to the appearance of a pathology whose symptoms will be relationship with the injured tissue(s). The stimulation is all the more accelerated as the « stress » of our life is intense (noise, shocks (sports), hectic life, unbalanced diet, nor adapted to our physiology, in particular that of our digestive system, etc.) . This does not imply the onset of a disease but the increasing life expectancy, the risk of onset of a chronic condition rises this is how we speak of degenerative diseases
The environment
- Air, water, Food
- high doses of pesticides (rotenone, ), heavy metals.
- médications : statines, anti-inflammatories, immunosuppressives,
- Affective and psychological
- efforts, physical shocks (great athletes, rugby, tennis, )
- viral (Covid 19), bacterial (post Lyme), parasitic (trypanosome, ) infections.
- latent chronic « infections » in the mucous membranes, mainly
Immunologic aspects :
- The immune system is primarily a surveillance system.
- Any antigenic modification (innate, acquired immunities) will be integrated by immunocompetent cells and visualized by the production of antibodies of defined isotype: A, M or G.
- The search for antibodies directed against epitopes or antigens allows the analysis of the antigenic modifications induced, and, consequently, a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms, particularly free radicals.
The discovery of antigenic communities between supernumerary proteins in serum and strains of Enterobacteriaceae suggests that bacterial components are very often the cause. Evidence for this is that these bacterial constituents, along with bacterial lipopolysaccharides or LPS (gram-), particles released into the intestinal lumen by all gram-negative infections are immunogenic .
Inflammation Aspect :
Following a localized or diffuse attack on the tissue, whether it be a traumatic shock or an infection of viral, parasitic or bacterial origin, a complex cascade of reactions is generated by the organism to eliminate the undesirable agent and makes it possible to implement the process of tissue repair.
This set of events defines the inflammatory reaction. The associated clinical and biological abnormalities constitute the inflammatory syndrome.
Cytokines are the main local and systemic actors at the origin of this syndrome.
The triggering of the inflammatory cascade has many origins :
- bacteria , viral, parasites, fungal;
- Tumoral ;
- traumatic (surgery, injuries, violent sports, ), physical (burns, radiation, etc.), tissue necrosis (ischemia, infarction);
- immunological (autoimmune, transplant rejection).
- In the Covid 19 most of the patient did die from the inflammation by reaction of the body against the virus
Cells of the monocyte-macrophage lineage, in particular macrophages and dendritic cells are our first lines of defense against these attacks.
Macrophages activated by the inflammatory cascade produce, depending on the conditions, many cytokines, and chemokines
These cytokines can induce the production of many pro-inflammatory factors such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes, platelets activating factor, proteases, and free radicals
One or more repetitive infection(s) associated with various environmental factors constitute the first phase of the pathology.
An inflammatory syndrome is associated, resulting in the activation of many transcription factors, in turn regulating a whole biochemical cascade of various events, linked only by their hypothetical organic origin.
Which can lead to the activation of endogenous factors (oncogenes, endogenous retroviruses…) which will over activate the transcription factors, increasing the inflammatory syndrome, the appearance of autoantigens and therefore autoantibodies and a disorganized lymphocyte response (T and CD8 mainly).
The exacerbation of the local inflammatory response is therefore associated with an excess of cytokine production.
These cytokines intervene on the hypothalamic-pituitary axis (appearance of fever) by inducing the production by the hypothalamus of « corticotropin releasing factor » (CRF) which acts on the cells of the pituitary gland to make them produce the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), the latter is responsible for the production of glucocorticoids by the adrenals.
Indeed, the results obtained on the nitrosylated amino acids are positive compared to the controls mainly in IGA (mucosal immunity).
The possible infiltration of cells of the monocyte-macrophage lineage or the presence of microglial cells in the central nervous system, activated it seems, could be the very first candidates for an important production of nitric oxide.
Their activation is obviously dependent on direct factors (circulating antigens, autocrine production of pro-inflammatory cytokines or chemokines) and/or indirect factors (lymphocyte signaling, intercellular communications).
High local productions of NO could be one of the aggravating factors of the disease. This radical would therefore be responsible for sustained neuro-inflammation (localized in certain areas of the CNS or not) and tissue destruction.
Tissue and cell destruction refers to the release of chemical compounds that could intervene in the maintenance of homeostasis, therefore of the various systems of the human body.
We must not forget that the dendritic cells are able to analyze our bacterial flora by emission of pseudopodia through the epithelial cells of our digestive tract and therefore to be informed of the commensal flora. Depending on the prevailing balance, they are able to activate and trigger a whole cascade of chemical signals.
Results showed that in parallel, we had an activation of the IDO pathways (leading to the synthesis of quinolinic acid), THO (leading to the synthesis of serotonin and melatonin), the anthranilic acid pathway and the acid pathway. kynurenic.
These pathways are activated by pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, like the NO synthase pathway.
These two pathways counterbalance each other in many pathologies. They differ in their mode of action:
The NO synthase pathway produces NO with cytostatic and cytotoxic effects against pathogens.
Tryptophan pathways limit the pool of tryptophan, an important element involved in the metabolism of pathogens: either to destroy them or to limit their proliferation.
Most derivatives of the tryptophan pathway are toxic substances for the organism.
Their accumulation in many cell populations of the central nervous system induces the establishment of apoptotic mechanisms.
What is the exact nature of the establishment of such biochemical mechanisms during the evolution of chronic diseases?
Like lipid A, a key fragment of bacterial GRAM lipopolysaccharides -, this structural subunit can activate the CD14 pathway in macrophages, directly linked to the NO synthase pathway.
Phospholipases C, adhesins and flagellins are also known for their major role in pro-inflammatory activation.
If the self-maintenance of chronic diseases is bacterial with the effect of a devalued intestinal flora, associated pathologies, diet, quality of life, pollution, the use of toxic products with strong persistence, all this leads to an imbalance commensal flora
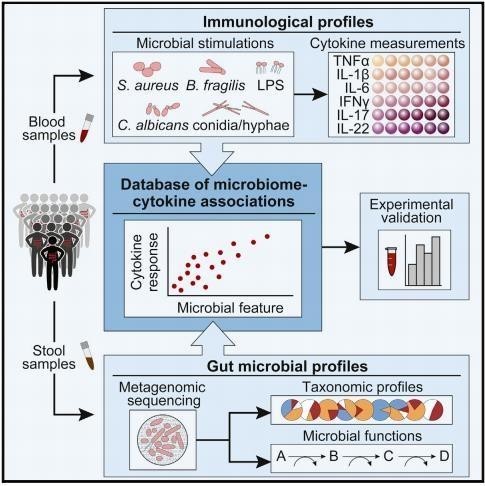
“Linking the Human Gut Microbiome to Inflammatory Cytokine Production Capacity The Broad
Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA 02142
Structure of the intestinal wall
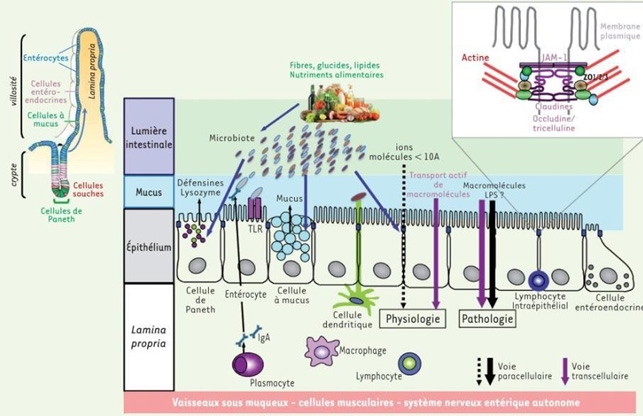
Here is how the intestinal wall plays its role but in the event of an imbalance linked to a variation in the microbiota, chemical agents, drugs, pathogens such as bacteria or viruses.
it occurs the opening of this barrier which is at the origin of all or almost all chronic diseases, Autoimmune, allergic or intolerance to Gluten for example and of the inflammatory reaction like the Cytokinic storm in covid 19.
For years our company has developed pharmaceutical compositions capable of reducing or blocking this mucosal hyperpermeability. The induced effects make it possible to stop the inflammatory and autoimmune effects and by preventing the passage of certain compounds such as LPS, the chronicity of neurodegenerative diseases is reduced.
The layer of cells called Enterocytes produce enzymes capable of cutting large molecules (lipids, carbohydrates, proteins) into small molecules (simple sugars, fatty acids, amino acids) which can be absorbed and enter the bloodstream.
This barrier is normally able to block unwanted molecules, bacteria…
Between each Enterocyte there is a space whose role is important is the tight junction. It is she who will control the permeability of the intestine. When it is altered and we will see how
afterwards, it lets macromolecules of chemical (pesticides), food (gluten) or bacterial origin (Lipopolysaccharides LPS) pass through
We then speak of intestinal hyperpermeability which causes inflammatory reactions, autoimmune or other diseases as one of the elements of the chronicity of Neurodegenerative diseases A protein -Zonuline is produced by the intestinal mucosa. Its alteration or degradation or the lack of fundamental components gives Zonuline the property of disassembling the tight junction.
Enterocytes are renewed every 36 hours. Due to rapid renewal, epithelial cells have a very high energy demand and Butyrate is the major energy substrate, nearly 70% of these needs.
The fermentation of starch, undigested in the upper part of the digestive tract and associated with fibers, leads to the production of short-chain fatty acids, butyrate, lactate, acetate and propionate. In addition, enterocytes use an elective fuel L-Glutamine brought by food of animal origin.
A diet rich in fiber and good quality protein is therefore essential if you want an efficient intestinal flora and an optimal colonic mucosa.
The intestinal flora constantly interacts with the intestinal immune system, with which it is in constant contact
The interaction between the enormous mass of antigens constituted by the intestinal microflora and the intestinal immune system is extremely complex, but in an organism in equilibrium it maintains a » immune background noise « , an essential balance between the bacteria in the flora and the immune system that regulates them
An imbalanced flora, called dysbiosis, leads to an exacerbated response of the intestinal immune system, increasing inflammation, which results in impaired tight junctions
The passage of fragments of walls of bacteria destroyed by the intestine, and passing into the general circulation, the endotoxins, is accompanied by the important secretion by the organism, and if the arrival of endotoxins is massive, can be the starting point of septic shock, respiratory distress, renal ischemia or cytokine storm
The dosage of endotoxins in the blood is a reliable marker of intestinal hyperpermeability The causes of intestinal hyperpermeability are extremely numerous:
Any disruption of the intestinal biotope, dysbiosis, leads to an immune system response, with the release of inflammatory cytokines, resulting in an inflammatory state of the small intestine and colon mucosa, with alteration of the epithelium.
The causes of this dysbiosis can be numerous:
- Stress, which greatly reduces the volume and quality of all digestive juices, stressed subjects also having insufficient chewing
- Antibiotic therapy
- infections , the most banal of gastroenteritis can have dreadful consequences
- Toxic chemical agents
The subject that governs our work today concerns Charcot’s disease or Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis disease which affects many athletes elsewhere in the USA it is called Lou Gehrig ‘s disease Baseball player unfortunately suffering from this disease.
It is known that during a prolonged sporting effort, the intestinal irrigation drops by 20%, the organism increasing the influx of blood to the muscular masses.
This sharp decrease in intestinal irrigation, ischemia, leads to a decrease in the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the intestinal cells, which can lead to local tissue damage.
But it is above all when the effort is stopped, when the normal visceral flow is restored, that the sudden increase in the supply of oxygen to the tissues causes a massive influx of free radicals which will damage the epithelial cells and tight junctions, leading to loss of mucosal seal.
The repetition of these episodes will perpetuate the damage to the cells, and therefore the intestinal hyper permeability. Runners, tennis players, rugby players are more exposed than cyclists, because the shock wave also plays an important role.
The massive influx of antigens into the organism due to the loss of tightness of the intestine will cause a multitude of clinical situations, and this according to the genetic capital of each individual and his past.
Disturbances will be expressed in the best of cases in the form of functional disorders, until the worst, in the form of autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases such as Charcot’s disease.
One of our Bordeaux friends died 2 years ago of Charcot’s disease. This 48-year-old sportsman and rugby player from Martinique had spent his youth in the banana fields in an environment rich in Chlordecone!!! this explains that??
The consequences of hyperpermeability in general
They affect the digestive system itself, and can be extra digestive, affecting the skin, joints, tendons, muscles, thyroid, lungs, nervous system, etc.
Intestinal hyperpermeability is found in all the following pathologies, even if it is not the only mechanism involved because they are most often multifactorial pathologies, but it must absolutely be taken into consideration:
– Some examples
Irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative – hemorrhagic recto colitis.
Digestive food allergies, respiratory allergies, asthma, eczema, urticaria, psoriasis, lupus erythematosus.
Rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, recurrent tendonitis Chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia
Thyroiditis, migraines
Autism, even certain psychiatric illnesses such as schizophrenia
Neuro-degenerative autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, Charcot’s disease,
Parkinson’s, and Alzheimer’s
CONCLUSIONS
We show that environmental, food, chemicals, virus… can have a strong impact on the gut balance.
This will be the initialization and create chronicity in many disease
We need to protect our Gut and its permeability which is at the origin of many disease
A recent study had shown that the Immune system is responsible of Alzheimer disease as initialization before it goes to the brain. The immune system is just next door to the gut!!
As well we show that after a ischemic stroke there a modification of the gut balance! Its like the egg and the Hen. The paradox can nevertheless be treated as a matter of very serious cosmogony!!
At the end we can say to protect your brain take care of your gut !!!
Dr Jean Pascal Zambaux


